- Explore the concept of diversity and intersectionality of identities
- Examining how power and privilege shaped libraries
- Understanding microaggressions/subtle acts of exclusion in the workplace
Saturday, November 05, 2022
Practicing Anti-Racism in Information Spaces: Notes From the Field
Thursday, August 25, 2022
The Importance of Inclusive Community Engagement & Equitable Participation in Programming
As a community engagement expert, having organized events over the past twenty years, it’s not difficult for me to put together a public program and speaker panel. It's second nature by now, having done it for so long. But as I reflect over the years, it was also easy to select a homogenous group, especially if a profession (such as libraries) tends to draw from a homogenous group itself.
Professional career coach Karen Catlin and author of Better Allies: Everyday Actions to Create Inclusive, Engaging Workplaces is an excellent reminder for event planners to be intentional and inclusive. She points out that there is even terminology out there. Did you know that “manel” is a term coined to describe a panel consisting only of men? It wasn’t too long ago that there were “manferences” featuring all-male speaker lineups. Another huge and ever-growing problem is the all-white panel, or “wanel.” Across industries, these exclusionary events have become ubiquitous for years.
Even more problematic is when these speakers don’t have directly lived experiences with the topic. Consider panels about challenges faced by POC or women featuring only men. Or discussions on transgender rights where all the panelists are cisgender people.
Most organizers reach out to their network to find people who can speak on the topic. If they lack diversity in their network, the likelihood is that they’re going to lack diversity at the event. Thus, ensuring that speakers represent a variety of viewpoints and life experiences should be a goal for all organizers. We should be willing to move outside our comfort zones. Some concrete suggestions for all who organize public events by Catlin:
- Inclusive speaker lineups - Be intentional in your selection. If you’re organizing an event, ask every male you’re inviting to speak to recommend a woman, a person of colour, or a member of another underrepresented group to also speak.
- Code of Conduct – Creating and enforcing a code of conduct. Having a diversity statement (such as this one from Word Vancouver Festival) clearly concretizes and makes clear the values of the organization.
- Inclusive Content - Ensure supportive measures so that presentations showcase diversity in slide decks. For example, the simple act of using stock photos and illustrations of people from underrepresented groups makes all the difference. Just as we make sure that the presentation works smoothly on technology, the same care should be made to the presentation itself.
Monday, August 15, 2022
Acting With Power, Power with Empathy
Power is a part of a social contract and as Stanford Graduate School of Business professor and psychologist Deborah Gruenfeld suggests, “People have power to the extent that others consent to being controlled.” Having been in a bureaucratic organization, I’ve seen firsthand how power influences decision-making, often letting personal and subjective impulses cut discard policy and common sense. Power doesn’t exist in a vacuum, but instead is contextual, and exists in relationships by virtue of the roles we play in each others’ lives. Power is often associated with Machiavellian ethics, ancient Legalist techniques, or Kissinger’s cynically “power is the ultimate elixir” maxim. But we should think of the power the other way: that it’s a part we play in someone else’s story.
Gruenfeld’s research and course at Stanford is sobering yet look into the art and science of power. The role of one’s power depends on who’s on the stage and what the story is. Rather than thinking of power as flowing to those who are the loudest or have the most impressive job title, power is how much we use, like actors do, in controlling the stage, which is why some struggle to step up and be taken more seriously while others are too aggressive and others too nice. While there is much to unpack in this two-decade-long research, three themes stand out for me in Acting With Power.
Responses to power – Aggressors, bureaucrats, and appeasers are three common responses to power and leadership. While aggressors are motivated to win approval from their peers to do the best of what they are asked to do in positions of power - often at the expense of those they are in charge of - bureaucrats are those who simply match expectations and follow rules to a T, being risk averse and have no aspirations to actually excel. The appeasers, in contrast, played nice and actually befriend their underlings and be liked. Do any of these traits relate to you?
Insecurity - Peeling back the darker veneer of the need for power is a story of insecurity. Whether it’s disinhibition, objectification, entitlement, megalomania, or bullying, abusers have a fundamental need for validation and stem from previous life experiences that deprived them. It’s an interesting psychoanalytical tool to examine how power corrupts, but Gruenfeld counsels that to wrangle a bully – disarm and detach from the abuse – one must reclaim one’s story and control of the plot. Realize that choices are available and we can choose how to respond to the bad actors who enter our realm. The way out is to focus on acting, on doing something, to step out of the role of victim. Choose your context carefully, police your borders, and don’t take the bait.
Culture of Beneficence – The book offers an antidote: beneficence - the developmental maturity to prioritize the welfare of the less powerful. We not only need to look for leaders with maturity whose ability to control selfish impulses while acting in ways to benefit others, but also enact those attributes ourselves. Rather than gaining power for personal advancement, a more mature approach to power is one that is based on lasting contributions to the organization and see power as a resource that is used to protect others rather than self-preservation. Those who give up their own resources to invest in group success with no promise of any return or personal benefit are often rewarded with more status. In evolution, it’s the only approach that makes sense, too.
As a visible minority from a historically underrepresented group, I’ve always felt that power has been fleeting. With context from critical race theory, one can see that power is inextricably more complicated with racialized and BIPOC actors. But I do believe that Gruenfeld’s message is a universal one: although we can all feel powerless, we always have more power than we think we do. We just need to play our roles.
Insecurity - Peeling back the darker veneer of the need for power is a story of insecurity. Whether it’s disinhibition, objectification, entitlement, megalomania, or bullying, abusers have a fundamental need for validation and stem from previous life experiences that deprived them. It’s an interesting psychoanalytical tool to examine how power corrupts, but Gruenfeld counsels that to wrangle a bully – disarm and detach from the abuse – one must reclaim one’s story and control of the plot. Realize that choices are available and we can choose how to respond to the bad actors who enter our realm. The way out is to focus on acting, on doing something, to step out of the role of victim. Choose your context carefully, police your borders, and don’t take the bait.
Culture of Beneficence – The book offers an antidote: beneficence - the developmental maturity to prioritize the welfare of the less powerful. We not only need to look for leaders with maturity whose ability to control selfish impulses while acting in ways to benefit others, but also enact those attributes ourselves. Rather than gaining power for personal advancement, a more mature approach to power is one that is based on lasting contributions to the organization and see power as a resource that is used to protect others rather than self-preservation. Those who give up their own resources to invest in group success with no promise of any return or personal benefit are often rewarded with more status. In evolution, it’s the only approach that makes sense, too.
As a visible minority from a historically underrepresented group, I’ve always felt that power has been fleeting. With context from critical race theory, one can see that power is inextricably more complicated with racialized and BIPOC actors. But I do believe that Gruenfeld’s message is a universal one: although we can all feel powerless, we always have more power than we think we do. We just need to play our roles.
Monday, July 11, 2022
The Racial Pay Gap - Much Work Remains to Be Done in Canadian Academic Libraries
“The Racial Pay Gap” indicates that there’s still much inequity in Canada’s academic libraries. While Canadian academic libraries have made progress in hiring and retaining employees from underrepresented groups, they still lack offering equitable salaries. My ViMLoC colleague, Yanli Li’s “Racial Pay Gap: An Analysis of CARL Libraries” is an alarming study on the racial pay gap of visible minority librarians. Using data from the 8Rs CARL Libraries Practitioner Survey in 2014, Li’s research study examined the impact of race on the earnings attainment process based on a sample of 392 CARL library practitioners and found a significant salary disparity between visible minorities and nonvisible minorities. It’s really important research that deserves more attention in our profession.
The study admits that because it is limited to 29 of the larger Canadian university libraries and two federal government libraries that comprise CARL. It would be interesting to study the racial salary gap of other university and college libraries or public libraries for a more comprehensive landscape of Canadian libraries. One can surmise that the racial pay gap probably exists in these institutions based on existing research. Perhaps a more in-depth examination of hiring, promotion, and access to senior positions, particularly the discrimination against visible minorities in the library science labor market, can also be done to further understand the specific factors of the racial salary gap.
While academic Research Libraries (ARL) in the US made great strides in the last three decades toward decreasing the racial pay gap, the same cannot be said about Canadian (CARL) libraries and this is surprisingly embarrassing, to say the least. As one social commentator pointed out once, comparing itself to the United States is almost like a national sport in Canada. Canadians revel at their superiority over their American counterparts, but when it comes to paying disparities, it’s business as usual. It’s remarkable how far Canadian academic libraries lag behind their American counterparts. As the authors of this study comment, “[o]verall, [American] ARL libraries have done an outstanding job of fostering racial equality in pay. . . there is no longer a statistically significant wage gap between nonminority and minority librarians in ARL libraries.” In fact, American counterparts have used more tools at their disposal for analysis, too. As opposed to using basic comparisons of group means to examine the racial salary gap in Canada, American studies have adopted multiple regression models to assess multiple variables of earnings in the library science labor market. All this is to say that much work remains for not only closing the racial pay gap in CARL libraries.
The study admits that because it is limited to 29 of the larger Canadian university libraries and two federal government libraries that comprise CARL. It would be interesting to study the racial salary gap of other university and college libraries or public libraries for a more comprehensive landscape of Canadian libraries. One can surmise that the racial pay gap probably exists in these institutions based on existing research. Perhaps a more in-depth examination of hiring, promotion, and access to senior positions, particularly the discrimination against visible minorities in the library science labor market, can also be done to further understand the specific factors of the racial salary gap.
While academic Research Libraries (ARL) in the US made great strides in the last three decades toward decreasing the racial pay gap, the same cannot be said about Canadian (CARL) libraries and this is surprisingly embarrassing, to say the least. As one social commentator pointed out once, comparing itself to the United States is almost like a national sport in Canada. Canadians revel at their superiority over their American counterparts, but when it comes to paying disparities, it’s business as usual. It’s remarkable how far Canadian academic libraries lag behind their American counterparts. As the authors of this study comment, “[o]verall, [American] ARL libraries have done an outstanding job of fostering racial equality in pay. . . there is no longer a statistically significant wage gap between nonminority and minority librarians in ARL libraries.” In fact, American counterparts have used more tools at their disposal for analysis, too. As opposed to using basic comparisons of group means to examine the racial salary gap in Canada, American studies have adopted multiple regression models to assess multiple variables of earnings in the library science labor market. All this is to say that much work remains for not only closing the racial pay gap in CARL libraries.
Saturday, July 02, 2022
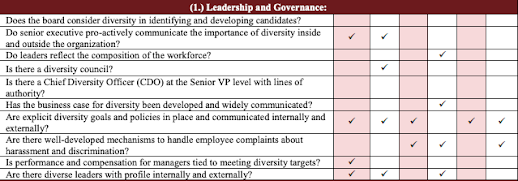
The Diversity Audit Tool (DAT)
A diversity assessment can measure an organization’s progress in increasing diversity not only within its human resources functions but also in its activities in the creation of products or services. While there is no shortage of diversity audit surveys out there, one, in particular, stands out to me and that is the Diversity Audit Tool (DAT) developed at the Diversity Institute at Toronto Metropolitan University. I like that it has been well used in examining both profit and non-profit organizations and adapted for use by many businesses over the years.
The DAT is a useful tool for assessing and identifying leading practices to increase diversity in organizations. The DAT was created by Ryerson University’s Diversity Institute, in partnership with Canadian Advanced Technology Alliance Women in Technology (CATAWiT) Forum, as part of a project on increasing women’s participation in the information and communications technology (ICT) sector, led by Wendy Cukier. The DAT is divided into six key organizational levels or functions:
- Leadership and governance – Success of diversity initiatives depends on senior management’s commitment to diversity in addition to the integration of diversity goals as part of the organization’s strategy
- Transparent HR practices – Identifies areas where organizations can increase diversity in recruitment, performance management, promotion, education, and knowledge building as well as training and development.
- Organizational culture & Quality of Life – Flexibility and ensuring that the organizational culture is inclusive and accommodates the divergent needs of its employees.
- Metrics – Used to track and measure progress relative to diversity goals.
- Integration into the Value Chain -- Diversity in product development, marketing and customer service programs, communication (both internally and externally), media buys, philanthropy, government relations, as well as in procurement decisions.
- Developing the pipeline – Develops a future workforce that is diverse and inclusive
Monday, June 13, 2022
Gatekeepers of Diversity in Publishing and Writing
I recently wrapped up an arts mentorship program at Centre A and worked with a diverse group of writers, and as a group, we explored the creative writing and publishing industry within the context of BIPOC artists. It’s good timing that the Diversity in Canadian Writing: A 2020-2021 Snapshot has been released. UBC creative writing professors Rhea Tregebov and Kevin Chong led the project and developed the survey design. The results were not surprising: the typical respondent, based on our survey data, was: female, white, in their 60s, living in Ontario, straight, cis-gendered, and able-bodied.
In our sessions, we explored how “diversity washing” has become simply producing literary texts that publishers want for mainstream, but Canadian publishing continues to lack diversity in staffing. The next generations of writers that I worked with show that there is an emergence of diverse authors, but they are still shut out by the literary gatekeepers as there is a shortage of diverse publishers, agents, and editors. In order for BIPOC writers to flourish, they need better representation in those fields to be supported.
“There needs to be more transparency when it comes to how books are promoted and advocated for, and sometimes this has less to do with literary merit and more to do with the PR machine behind the book. This leaves a lot of us out, especially when we already face systemic barriers. We need opportunities to feature our work in more meaningful ways, beyond conversations about our identity and deeper into craft. […] It’s important that these questions are addressed by the publishing industry so that we can have transparency around what needs to be done.”
- Gatekeepers – Those in positions of power in the sector need to be more diverse, both within publishing houses and in affiliated organizations such as reviewing outlets, festival and prize administration, literary agencies and funding institutions, by creating concrete, transparent and measurable goals around their makeup
- Smaller Presses – Create greater systemic support for them which often are key in recognizing and promoting marginalized authors.
- Training - Mandate EDI training for staff, as well as create a budget and established procedure for employment of sensitivity readers among publishers.
- No More Identity Labels – Titles by marginalized authors should be promoted, evaluated and featured in nuanced, complex and meaningful ways beyond simple identity labels. Organizations, reviewers and readers should recognize that non-dominant culture content is not of limited interest and that publications are not limited by simple identity labels. Content should not have to be trauma-generated or otherwise identity-specific in order for authors to be given a platform.
- Funding – Create funding structures for disabled writers to pay upfront for the support needed to fully participate in events.
- Prizes – Carefully review the creation of new prizes, their mandates and their selection processes to ensure better inclusivity. Moreover, residency and grant opportunities that set an arbitrary age limit for eligibility should be removed.
I’m heartened by the work that the authors of this report and I’m optimistic that it puts the lens of EDI squarely focused on the current landscape of Canadian publishing. I’m often invited to government book awards and grant juries for diversity, consult on EDI by book publishers or join EDI committees. While I’m happy to participate and make a difference, I feel that my role is really at end of the conversation, to ensure representation, but not at the beginning, such as systemic change. It’s about time that EDI is integrated so that box-ticking exercises don’t need to be left at the end, as an afterthought. When I ended my final session of the Arts Writing Mentorship Program, I was heartened that participants understood that they were the next generation of the publishing industry, whether they are writers or acquisitions editors – and had a responsibility to instill change.
Sunday, May 22, 2022
Everything Will Be, Will Be in Chinatown - Honouring Asian Heritage Month
Thank you to the NFB, for sharing this film with us. I recall during my early days of community engagement and outreach work that the goal of Asian Heritage Month was to "celebrate" the successes of Asians in Canada. The complicated history of Canadians of Asian heritage or mixed-race heritage has often been obsfucated by the model minority myth and problems of anti-Asian racism covered and blurred. Since the pandemic, anti-Asian racism has skyrocketed and with one city called the anti-Asian hate crime capital of the world. The 1907 riots in Vancouver is but one unfortunate historical incident among countless ones during the formation of the colonial settler society of North America. This video is an excellent reminder that the history that we forget continues to haunt us in the present day.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)